1 武汉大学遥感信息工程学院, 湖北 武汉 430079
2 中国地质大学 (武汉) 地球物理与空间信息学院, 湖北 武汉 430074
3 生态环境部卫星环境应用中心, 北京 100094
4 武汉大学测绘遥感信息工程国家重点实验室, 湖北 武汉 430079
5 武汉大学电子信息学院, 湖北 武汉 430079
煤矿开采是最重要的甲烷排放源, 然而其排放清单的准确性很低, 一个关键的原因在于缺乏精准识别和定位该类排放源的能力。近年来, 前沿研究表明可以利用卫星高光谱数据反演高分辨率的甲烷异常, 从而帮助识别排放源。但是, 在地表类型复杂地区该算法会完全失效。针对这一问题, 率先提出一种基于 L1 重加权和迭代收缩阈值算法 (ISTA) 匹配滤波器的算法。利用高分五号 (GF-5) 数据在山西地区的实验表明, 该方法性能显著优于现有的其他方法。实验中, 本方法识别出 23 个甲烷强点源, 这些点源全部位于 TROPOMI 的甲烷高值区内, 且高分辨遥感影像显示这些点源处存在典型的煤矿开采设施。该方法的提出为利用 GF-5 卫星数据在世界范围实现甲烷点源排查奠定了技术基础。
甲烷柱浓度异常探测 基于 L1 重加权和迭代收缩阈值算法的匹配滤波器算法 高分五号可见光短波红外高光谱相机数据 XCH 4 anomaly detection L1 reweighted iterative shrinkage thresholding alg GF-5 visible-shortwave infrared advanced hyperspec 大气与环境光学学报
2022, 17(6): 670
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping, and Remote Sensing, Wuhan University,129 Luoyu Road, Wuhan 430079, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Geospatial Technology, 129 Luoyu Road, Wuhan 430079, China
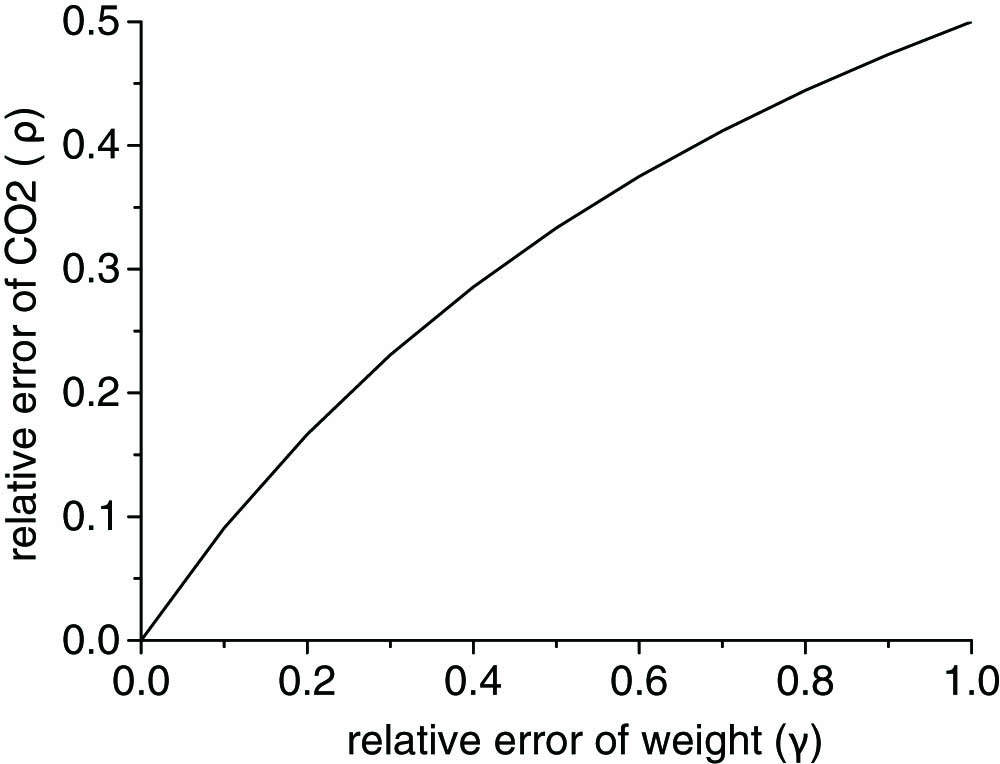
Accurately measuring the differential molecular absorption cross section is the key to obtaining a high-precision concentration of atmospheric trace gases in a differential absorption lidar (DIAL) system. However, the CO2 absorption line is meticulous at 1.6 μm, easily translating and broadening because of the change of temperature and pressure. Hence, measuring the vertical profile of atmospheric temperature and pressure to calculate the vertical profile of the CO2 weight parameter is necessary. In general, measuring atmospheric temperature and pressure has a certain amount of uncertainty. Therefore, this study proposes the concept of a balanced on-line wavelength, where the differential molecular absorption cross section is larger and the CO2 weight parameter is insensitive to the uncertainty of atmospheric temperature and pressure. In this study, we analyzed the influence of uncertainty on the CO2 weight parameter at every preselected wavelength, as well as determined an appropriate wavelength near one of the absorption peaks. Our result shows that 1572.023 nm should be one of the appropriate balanced online wavelengths. The measurement errors of the mixing ratio of CO2 molecule in this wavelength are only 0.23% and 0.25% and are caused by 1 K temperature error and 1 hPa pressure error, respectively. This achievement of a balanced on-line wavelength will not only depress the requirement of the laser’s frequency stabilization but also the demand for measurement precision of the atmospheric temperature and pressure profile. Furthermore, this study can achieve the exact measurement of the vertical profile of atmospheric CO2 based on an independent differential absorption laser.
Atmospheric optics Lidar Photonics Research
2015, 3(4): 04000146





